The right hemisphere can juggle multiple ambiguous possibilities and interpretations, whereas the left hemisphere jumps to premature conclusions
When guessing a sequence, the left hemisphere will choose a strategy even at the expense of getting things wrong, and When flashing lights were changed to follow whatever strategy was being used to guess them, the left hemisphere will insist that it had just cracked the sequence. So the left hemisphere needs certainty and needs to be right. The right hemisphere makes it possible to hold several ambiguous possibilities in suspension together without premature closure on one outcome. The right prefrontal cortex is essential for dealing with incomplete information and has a critical role to play in reasoning about incompletely specified situations. The right hemisphere is able to maintain ambiguous mental representations in the face of a tendency to premature over-interpretation by the left hemisphere.
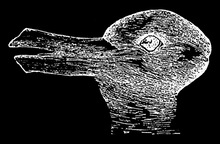
The right hemisphere’s tolerance of uncertainty is implied everywhere in its subtle ability to use metaphor (The right hemisphere is responsible for the capacity to understand metaphor), irony and humor, all of which depend on not prematurely resolving ambiguities. So, of course, does poetry, which relies on right hemisphere language capacities. During ambiguous stimulation of perceptual rivalry (the phenomenon of an ambiguous figure that can be seen in one way or another, but not both simultaneously, such as the duck–rabbit above or the Necker cube) right frontal cortex is more active.

References
- Mcgilchrist, Iain. (2010). The Master and His Emissary Chapter 2 What Do the Hemispheres Do (p. 166). London, UK: Yale University Press.
Metadata
Type:🔴 Tags: Biology / Neuroscience / Neuropsychology Status:☀️